🐳Two-Tier Application Deployment with Docker
"Efficiently Scaling and Managing Applications with Docker: Two-Tier Deployment Approach" 🐋 · ☸️ · 🚢 · 🐬 · ☸ · 🚀 · ⚓
🌌First Let's go through the overview.
I've been working on deploying a 2-tier Flask application using Docker. First, I containerized the application and then pushed the image to Docker Hub. For the database, I decided to go with MySQL. To simplify the management of the containers and ensure they're on the same network, I used Docker Compose. This setup has made deploying and managing the application's components much easier. With Docker Compose, I could define all the services, networks, and volumes in a single file, streamlining the deployment process. Pushing the Docker image to Docker Hub also means that I can deploy the application on any machine with Docker installed with ease. MySQL provides a reliable and scalable data storage solution for my application. Overall, leveraging Docker's containerization technology and Docker Compose's orchestration capabilities has allowed me to create a robust and scalable deployment environment for my Flask application.
🌌Let's understand which Tools & Technology we need to make this application
👨💻EC2
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) is a web service that provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud.
👨💻GitHub
It is a web-based platform used for version control and collaboration on software development projects.
Here are some key features of GitHub:
Version Control: GitHub uses Git, a distributed version control system, to track changes to files and manage different versions of a project. Developers can create branches to work on new features or fixes and merge them back into the main branch when ready.
Collaboration: GitHub facilitates collaboration among team members by allowing them to review and discuss code changes, suggest improvements, and track issues and bugs using the built-in issue tracking system.
Code Hosting: GitHub provides a place to host code repositories, making it easy for developers to share their code with others and contribute to open-source projects.
Integration: GitHub integrates with a wide range of development tools and services, such as continuous integration (CI) systems, project management tools, and code editors, to streamline the development workflow.
Community: GitHub has a large and active community of developers, making it a valuable resource for learning, sharing knowledge, and finding solutions to coding problems.
Overall, GitHub is a powerful platform that helps developers collaborate on projects, manage code changes, and build software more efficiently.
👨💻Docker
It is a platform and tool that allows you to develop, deploy, and run applications inside containers.
👨💻Dockerfile
A Dockerfile is a text document that contains a set of instructions for building a Docker image.
👨💻Docker Image
A Docker image is a lightweight, standalone, executable package that contains everything needed to run a piece of software, including the code, runtime, libraries, dependencies, and configuration files.
👨💻Docker-compose
Docker Compose is a tool provided by Docker that allows you to define and run multi-container Docker applications. It uses a YAML file (docker-compose.yml) to configure the services, networks, and volumes for your application, making it easy to manage complex Docker environments.
👨💻Docker Hub
Docker Hub is a cloud-based registry service provided by Docker that allows you to store and share Docker images.
👨💻Docker Volume
In Docker, a volume is a way to persist data generated by and used by Docker containers. Volumes are stored outside the container's filesystem.
Here are some key points about Docker volumes:
Persistent Storage: Volumes provide a way to store data generated by containers persistently.
Shared Data: Volumes can be shared between containers.
Mount Points: Volumes are mounted into containers as directories.
Types of Volumes: Docker supports several types of volumes, including host-mounted volumes, named volumes, and anonymous volumes. Each type has its own use cases and benefits.
Managing Volumes: Volumes can be managed using the Docker CLI or through Docker Compose. You can create, inspect, remove, and manage volumes using these tools.
Overall, Docker volumes provide a flexible and convenient way to manage persistent data in Docker containers, making it easier to build and deploy applications that require persistent storage.
👨💻MYSQL
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) that is widely used for building scalable, high-performance web applications. It is known for its reliability, easE of use. it uses Structured Query Language (SQL)
Some key features of MySQL include:
Relational Database: MySQL is a relational database, which means that it stores data in tables with rows and columns.
Scalability: MySQL is designed to scale from small, single-user applications to large, multi-user applications.
Ease of Use: MySQL is known for its ease of use, with a simple installation process and a user-friendly interface for managing databases.
Compatibility: MySQL is compatible with many operating systems and programming languages, making it easy to integrate with existing systems and applications.
🌌Now, Here we go through the 2-Tier Application Deployment with Docker
We will see how to troubleshoot while making the 2-Tier App.
✔️Login to AWS Console.
✔️Search EC2 & Click on Launch Instances.
✔️Fill the form 1) Name of Instance 2) Select Ubuntu Image 3) Instance Type- t2.micro 4) Create New Key-Pair 5) Launch Instance.
✔️Connect the Instance-> You'll get Ubuntu Terminal.
✔️Update the System & Install Docker.
sudo apt-get update # Update the System
sudp apt-get install docker.io # Install Docker
✔️Changes the Ownership of the Docker socket file to the current user.
sudo chown $USER /var/run/docker.sock
✔️To Check the List of the Container.
docker ps # Check list of container
✔️Then Go to GitHub, Clone the Repository.
✔️Check the Repository clone or not.
ls # listing the directory.
✔️Change the Directory.
cd two-tier-flask-app/ # Your Clone Directory Name
✔️Make Dockerfile.
# Use an official Python runtime as the base image
FROM python:3.9-slim
# Set the working directory in the container
WORKDIR /app
# install required packages for system
RUN apt-get update \
&& apt-get upgrade -y \
&& apt-get install -y gcc default-libmysqlclient-dev pkg-config \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# Copy the requirements file into the container
COPY requirements.txt .
# Install app dependencies
RUN pip install mysqlclient
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
# Copy the rest of the application code
COPY . .
# Specify the command to run your application
CMD ["python", "app.py"]
✔️Now, Build Dockerfile.
docker build . -t flaskapp
✔️Check the Image of flaskapp
docker images # To check the images
✔️Now, go to your EC2 instance security group open port no. 5000 & save it.
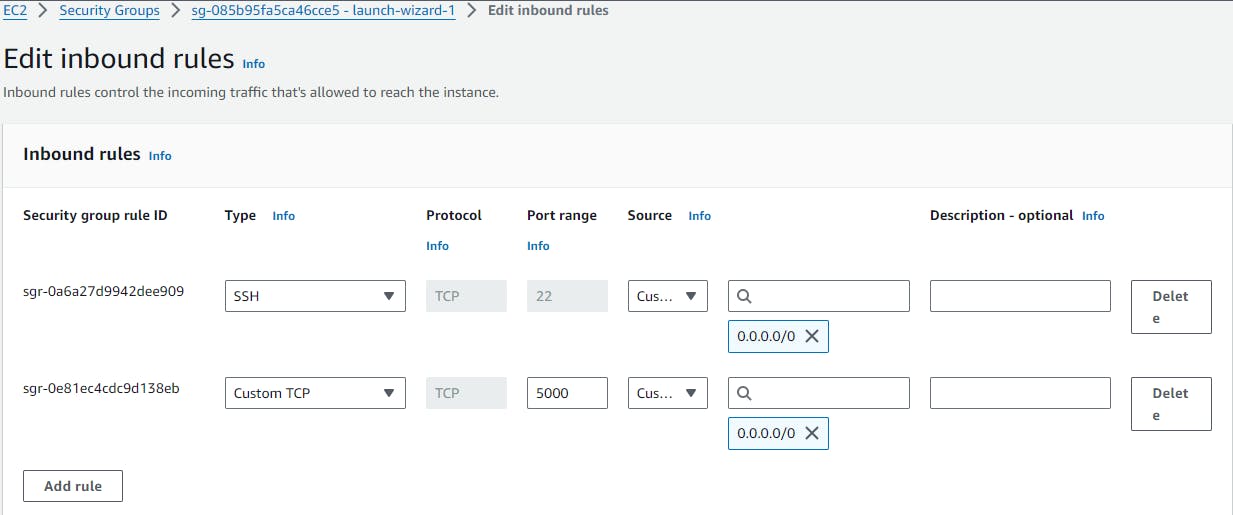
✔️Now run the container of flaskapp
docker run -d -p 5000:5000 flaskapp:latest
✔️Then for collecting data of flaskapp Mysql connect through local server
docker run -d -p 3306:3306 --name mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD="admin" mysql:5.7
✔️To check containers running or not
docker ps
✔️Now both containers are running on different Network so, create network to add both container in 1 network.
docker network create twotier # Two tier is network name(you can change network name)
✔️Now, kill the both containers that are not in same network.
docker kill <containerID> # you can kill muiltiple containers, you just add container_ID one by one
✔️Check, Now Images will get empty.
docker images
✔️Then, once again to attach both containers in same network.
docker run -d -p 5000:5000 --network=twotier -e MYSQL_HOST=mysql -e MYSQL_USER=admin -e MYSQL_PASSWORD=admin -e MYSQL_DB=myDb flaskapp:latest #to attach in same network
docker run -d -p 3306:3306 --network=twotier -e MYSQL_DATABASE=myDb -e MYSQL_USER=admin -e MYSQL_PASSWORD=admin -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=admin mysql:5.7 #to attach in same network
✔️Check, whether both containers are in same network or not
docker network ls
✔️To Inspect twotier network but, Still it shows container name different.
docker network inspect twotier
✔️So, Once again kill the both containers
docker kill <containerID>
✔️Run the both container again
docker run -d -p 5000:5000 --network=twotier -e MYSQL_HOST=mysql -e MYSQL_USER=admin -e MYSQL_PASSWORD=admin -e MYSQL_DB=myDb --name=flaskapp flaskapp:latest # run again container
docker run -d -p 3306:3306 --network=twotier -e MYSQL_DATABASE=myDb -e MYSQL_USER=admin -e MYSQL_PASSWORD=admin -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=admin --name=mysql mysql:5.7 # run the container if not work then remove old mysql container and run again mysql container
✔️Now, to go into Mysql database
docker exec -it <containerID> bash # your containerID will be different
✔️Enter the Password to enter into the database
mysql -u root -p # when you press the enter then give password to them. You can enter mysql database
✔️To check all datases in MYSQL.
show databases;
✔️To use particular database.
use myDb; # myDb is particular database name
✔️Now in myDb database Create Table Messages & run it.
CREATE TABLE messages (id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, message TEXT); #syntax of create a table in database
✔️Now access your flaskapp using your EC2 public-ip:5000 & write something.
✔️You can check your data will get save in table.
select * from messages; # to check all data of the table
✔️To exit from database.
exit
✔️If you want to save your flaskapp image in Dockerhub, login to dockerhub.
docker login # Give username & password of your dockerhub
#Once login succeeded
✔️Now tag your image to username of docker with image name
docker tag flaskapp:latest dockerwithalmas/flaskapp:latest
✔️You can see image with your username
COPY
docker images
✔️Let's try to push image on dockerhub.
COPY
docker push dockerwithalmas /flaskapp:latest
✔️Check with your dockerhub.

✔️If you want to run both containers in one command - flaskapp, mysql.
Install docker-compose.
sudo apt-get install docker-compose -y
✔️Make docker-compose.yml file.
version: '3'
services:
backend:
build:
context: .
ports:
- "5000:5000"
environment:
MYSQL_HOST: mysql
MYSQL_USER: admin
MYSQL_PASSWORD: admin
MYSQL_DB: myDb
depends_on:
- mysql
mysql:
image: mysql:5.7
ports:
- "3306:3306"
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: root
MYSQL_DATABASE: myDb
MYSQL_USER: admin
MYSQL_PASSWORD: admin
volumes:
- ./message.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/message.sql # Mount sql script into container's /docker-entrypoint-initdb.d directory to get table automatically created
- mysql-data:/var/lib/mysql # Mount the volume for MySQL data storage
volumes:
mysql-data:
✔️check docker container
docker ps
✔️Once again Kill & Remove both containers
docker kill <containerID> # kill both containers
docker rm <containerID> # remove both containers
✔️Now run docker-compose command. It will create network automatically.
docker-compose up -d # it creates network automatically.
docker-compose down # it down the access
✔️Finally, access your flask app -> publicip:5000

🎊This FlaskApp access under the one network..
I believe this blog will be really helpful, giving you fresh perspectives and teaching you something new and interesting. 🙏
😊 Enjoy learning!